The Philippine e-commerce sector is poised to surge in value to P969 billion by 2026 as more Filipino shoppers prefer to shop online. This booming market offers many opportunities for online retailers and for businesses. Unfortunately, this growth also presents the same level of opportunities for e-commerce scam artists and fraudulent groups who target online stores and customers.
According to recent data from Statista, online shopping scams made up 38% of all reported scams worldwide in 2020. Adding to the concern, Juniper Research paints a more alarming picture, forecasting that total merchant losses due to online payment fraud will surpass $343 billion from 2023 to 2027.
E-commerce scams continue to evolve, posing new threats to online store owners. To protect your business and customers, it’s important to be aware of common types of e-commerce fraud. In this article, we will explain how these malicious activities work, so you can avoid falling victim to them.
The State of E-commerce Fraud in the Philippines

Filipino online consumers have been targeted by different frauds since the e-commerce sector exploded in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A study conducted by TransUnion revealed that 44% of consumers in the Philippines were targeted by digital fraud in March of 2021. It was a 33% increase from the same period in 2019 and 2020.
The study also highlighted that scam artists and fraudsters didn’t only target individuals but also e-commerce businesses, with digital fraud attempts against businesses increasing by 31%.
The trend of e-commerce fraud in the Philippines persists even after the pandemic. In fact, a recent survey by the Global Anti-Scam Alliance (GASA) found that the country has the highest rate of online shopping scams among 11 economies in Asia.
The Philippines led the group with a shopping scam rate of 35.9%, followed by mainland China with 27.2%.
Filipinos Are Easy Prey for Internet Scams

A study commissioned by the Global Anti-Scam Alliance (GASA) and Taiwan-based tech security company Gogolook revealed that Filipinos tend to have confidence in their ability to spot scams.
The Philippines ranked third in the confidence category, trailing behind Indonesia at No. 1 and China at No. 2.
However, Filipinos may have overestimated their ability to spot online shopping scams and fraud.
In the first eight months of 2023 alone, reports indicated that Filipinos lost at least P155.20 million due to scams.
Meanwhile, an article from Nikkei Asia labels the Philippines as ‘Asia’s worst for online sales scams,’ emphasizing the lack of digital literacy and cybercrime awareness among Filipinos as aggravating factors.
According to the Asia Scam Report, 24.8% of Filipino victims respond too quickly to scammers’ demands, while 21.1% choose to take risks despite uncertainty about the potential dangers.
7 Most Common Fraud and Scams that Target E-commerce

The best way to avoid e-commerce fraud is to understand how it works. So, read along to find out the most common frauds and scams that target e-commerce businesses.
1. Card Not Present Fraud
Credit Not Present (CNP) is one of the most perilous types of e-commerce fraud, persistently harming the online shopping ecosystem. In the US alone, CNP fraud accounted for $8.75 billion in payment fraud losses. By 2024, experts anticipate that this fraud will cause $10.16 billion in losses.
CNP Fraud is a form of payment scam. It takes place when a fraudster illicitly acquires payment information and uses it without the cardholder’s consent
The cardholder has a certain level of security thanks to the chargeback policy offered by banks. In essence, a chargeback occurs when a customer disputes a credit card transaction, seeking a reversal through their bank.
Now, what happens to the online merchant who initially accepted the order, only to find it later flagged as fraudulent?
In this scenario, the customer’s card issuer issues a chargeback to the merchant, deducting the disputed amount along with a processing fee. This situation can lead to financial losses for the merchant, similar to the impact of a lost sale.
2. Friendly Fraud
Friendly Fraud occurs when a customer claims non-delivery or damage to an item they’ve paid for. To resolve the issue, the e-commerce business then has to refund, re-deliver, or face a chargeback.
Now, this can happen by mistake or intentionally. Let’s explain that in different scenarios:
- The customer sought a refund due to dissatisfaction with their purchase.
- A customer requested a chargeback for an unfamiliar bank statement.
- The customer is expecting a refund but hasn’t received it yet.
- The customer was billed multiple times for a single purchase.
- Unscrupulous customers aim to receive an item, falsely claim non-arrival, and request a refund.
As mentioned, Friendly Fraud may also tied to the utilization of chargebacks. Here fraudsters may bypass the merchant and seek chargeback directly to the bank. As the merchant, it’s your responsibility to prove the bad intention of the cardholder to dispute the chargeback.
3. Phishing Scams
A phishing scam is a fraudulent activity where cybercriminals use certain tactics to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information. This e-commerce fraud can occur in various channels such as emails, phone calls, text messages, or other means.
Phishing scams can appear very realistic and target both consumers and online merchants. Once successful, cybercriminals can make unauthorized withdrawals or exploit the obtained sensitive information.
Keep in mind that phishing scams change from time to time. Cybercriminals often adapt their tactics to stay ahead of security measures. The screenshot below serves as an example of phishing attempts on Facebook business accounts, illustrating the diverse forms these scams can take.
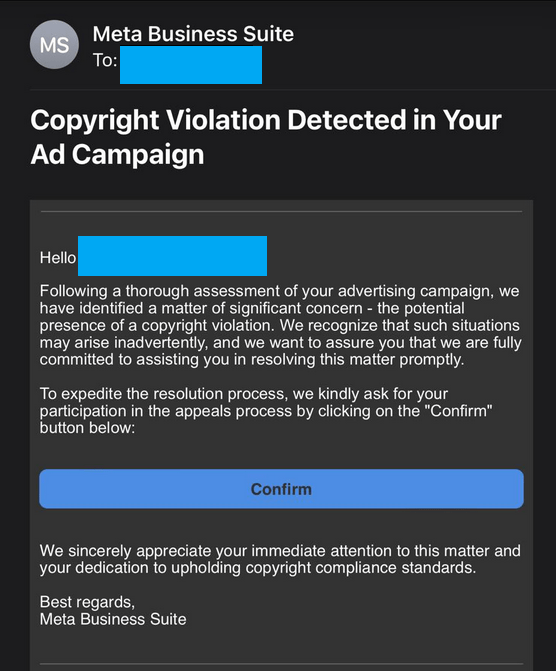
While phishing scams evolve, certain red flags remain consistent. To identify phishing scams, watch out for these signs:
- Claims of noticing suspicious account activity
- Stating issues with your account or payment information
- Insistence on confirming personal information
- Encouragement to click a link for payment or personal details
- Offering coupons or special deals that are too good to be true
To protect your community and audience, make sure that they are well informed about ongoing phishing activities online.
Taking the time to educate them about these e-commerce frauds is also an opportunity for you to demonstrate that you care.
4. Triangulation Fraud
Triangulation Fraud is a complex type of e-commerce fraud. As the name suggests, there are three main players involved: unsuspecting customers, legitimate e-commerce stores, and fraudsters. Here’s how Triangulation Fraud works:
Level 1: Scammer Setup a Fake Store
Triangulation Fraud starts with the Fraudster creating a fake storefront to get the credit card information of the unsuspecting victim. This storefront looks legitimate. In some cases, fraudsters even copy an actual e-commerce store. Moreover, to attract attention, this fake online store usually offers huge discounts.
Level 2: Unsuspecting Shopper Buys Item
Once a customer places an order on this deceptive platform, they unwittingly provide personal and payment information.
Level 3: Order Relay
The fraudster then uses this payment information to buy the same product from a legitimate e-commerce store and use the customer’s shipping address.
Level 4: Unsuspecting Shopping
The customer receives the product they ordered from the fake online store, which adds to the confusion. Since they get what they paid for, they may not immediately recognize the unauthorized nature of the second transaction.
Level 5: Discovering Unauthorized Transactions
The customer may discover the unauthorized transactions when they review their credit card statement and notice multiple charges for the same item, with one charge going to the scammer (fake online store) and another to the legitimate online seller.
Level 6: Impact on Legitimate Seller
At this point, the customer will initiate a chargeback which can result in the e-commerce store losing the payment. The merchant will have to cover also the chargeback fees. On the other hand, the fraudster may be able to use again the customer’s information for another scheme.
5. Affiliate Fraud
Do you operate an affiliate marketing program? This digital marketing strategy works wonders for many brands, regardless of their size. However, when a fraudster is involved, there’s always a risk you have to face.
Affiliate fraud occurs when individuals with malicious intent manipulate traffic and sign-ups to deceive merchants into believing they are receiving consumer attention that does not actually exist.
Fraudsters use different tactics such as using automated scripts, fake referrals, and other manipulative tactics. Affiliate fraud can range from simple actions like refreshing a webpage multiple times to more sophisticated methods such as sending spam emails and pop-ups, all of which aim to create misleading impressions of heavy traffic.
6. Google Ads Click Fraud
Google Ads Click Fraud operates similarly to affiliate fraud. This type of e-commerce fraud happens when a malicious actor deliberately induces a surge in clicks on your pay-per-click (PPC) ads, leading to increased advertising charges that deplete your marketing budget.
Perpetrators of Google Ads click fraud may include competitors, click bots, web crawlers, or click farms. One reason this deceptive practice happens is because the fraudster wants to deplete your budget, allowing them to secure the top advertising position.
Interestingly, you can also be the perpetrator of Google Ads Click Fraud to your own business. This happens when you unwittingly click your Google Ad repeatedly.
Fortunately, Google Ads now offers an anti-click fraud program to mitigate instances of click fraud. This program uses machine learning to identify and filter out invalid clicks before advertisers incur charges. Additionally, users have the option to report any suspicious activity to Google Ads for further review.
7. Coupon Abuse Fraud
Bonus Abuse Fraud is a straightforward form of e-commerce scam but can bring serious consequences if not detected promptly.
Coupon abuse fraud involves various tactics aimed at exploiting or manipulating coupon systems. Sadly, even your customers may engage in this practice to gain unauthorized benefits.
For instance, some individuals may exploit bulk purchase discounts by creating multiple accounts to make repetitive purchases.
In cases where a referral program offers discounts for bringing in new customers, fraudsters may create fake referrals or accounts to claim these discounts without genuinely referring new customers.
The good news is that you can combat these abuses by assigning unique coupon codes to individual users and transactions. Additionally, you can set a usage limit per customer. Finally, implementing authentication measures to verify user identities can further enhance security.
Fortify Your E-commerce Operation
E-commerce fraud and scams come in many shapes and sizes. They can damage your reputation and revenue in many ways. That’s why you need to know how to protect your online business with the most advanced security solutions and best practices.
Be Global E-commerce Corporation can help you secure your every e-commerce transaction. We offer you the latest technologies and tools to safeguard your website and transactions from malicious attacks and fraudsters.
Don’t leave your e-commerce operation vulnerable to various online frauds and scams. Contact us today and let us help you strengthen your online security and boost your business performance.





